SCIENCE
RETHINKING CYTOLOGY
Cytology – or cytopathology – is the art of diagnosing diseases by examining single atypical cells or cell clusters, as often found in fluid specimens.
Cytological testing is integral to modern cancer diagnostics due to its less invasive nature compared with biopsy, high reliability and low cost. [1]
Despite significant advances in medical technology, however, cytological samples still require extensive manual preparation and analysis – slowing down diagnoses and therapeutic decision-making.
At X-ZELL, our mission is to cut out time-consuming preparatory work and digitise sample analytics to take the art of cytology to the next level.
The result? Accurate early cancer detection that is accessible to everyone, anywhere.
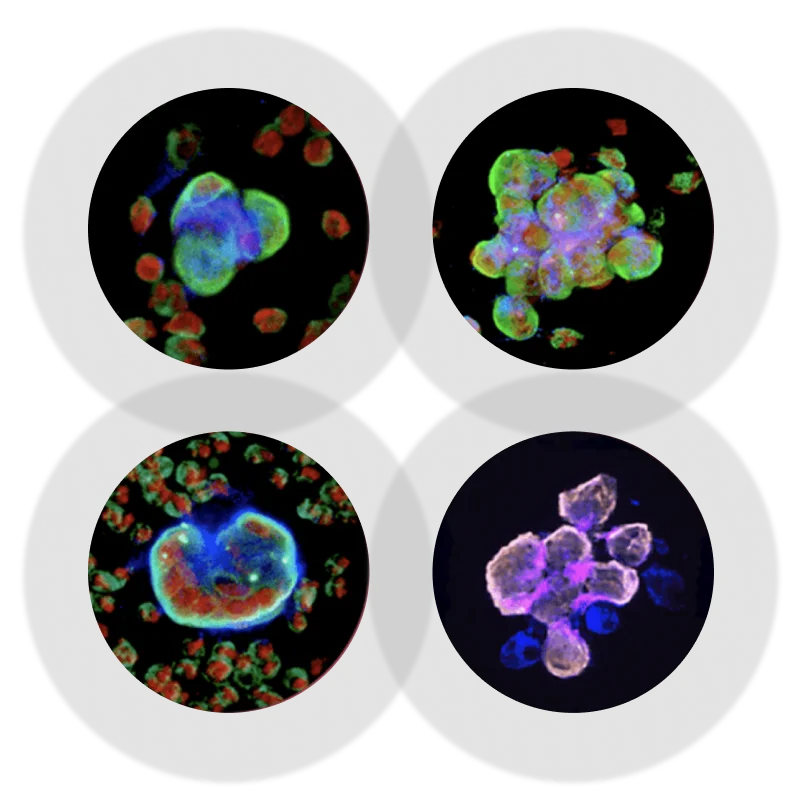
Pipeline
X-ZELL is collaborating with Singapore General Hospital (SGH) and the National University Hospital Singapore (NUH) to explore how X-ZELL single-cell diagnostics may aid in the early detection of clinically significant prostate cancer in whole blood.
The prospectively blinded, 400-patient multi-centre study officially commenced in 2020 and will lay the foundation for the launch of a commercially available blood test in the future.
- \In collaboration with Diagnostics Development Hub Singapore
- \Pilot study showed more than 70 per cent reduction in unnecessary biopsies [2]
- \Interim publication expected in 2024
² Bhakdi et al. 2019
Note: Cytopathology is only one of several tools to confirm the presence of cancer and should be supported by physical examination and medical imaging, such as ultrasound, CT scan or MRI scan. Unless specifically indicated, all X-ZELL products are designated as general laboratory equipment.
X-ZELL Publications
Bhakdi et al. Multiplexing Immunodiagnostics of Liquid Cytology Samples. Transitioning away from Cytoblocks (abstract, ECC 2023) Cytopathology 2023
Bhakdi et al. Immunocytomorphological landscape of tCAC in the blood of lung cancer patients (abstract, ECC 2021) Advances in Clinical and Experimental Medicine 2021
Narula et al. Slide-based immunocytometry for diagnostics of acute leukemia (abstract, Blood 2021) Blood 2021 Abstract Book 2021
Bhakdi et al. Improved analysis of tumour-associated circulating rare cells (abstract, ECP 2021) Virchows Archiv 2021
Chiangjong et. al. Cell-main spectra profile screening technique in simulation of CTC using MALDI-TOF Cancers 2021
Bhakdi et al. Cytomorphologic and immunophenotypic characterization of tCAC in prostate adenocarcinoma (abstract, ECP 2020) Virchows Archiv 2020
Bhakdi et al. Accuracy of tCEC as a screening biomarker for clinically significant prostate cancer Cancers 2019
Bhakdi & Thaicharoen Easy employment and crosstalk-free detection of seven fluorophores in a widefield fluorescence microscope Methods & Protocols 2018
Bhakdi Tumour-derived circulating endothelial cells predict clinically significant prostate carcinoma (abstract, APCC 2018) BJU International 2018
Waseem et al. Buffer-optimized high-gradient magnetic separation for isolation of plasmodium-infected RBC Journal of Magnetics 2016
Waseem et al. Antibody-conjugated paramagnetic nanobeads: Kinetics of bead-cell binding International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2014
Bhakdi et al. Optimized high-gradient magnetic separation for isolation of plasmodium-infected RBC Malaria Journal 2010
¹ X-ZELL data. More information upon request
© 2024 X-ZELL Biotech Pte. Ltd.
Find Us